Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Na
Na )TiO
)TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Aoyagi, Rintaro*; Fu, D.*; Takenaka, Tadashi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 39(3), p.247 - 250, 2014/09
Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO are
are 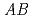 O
O perovskite ferroelectric materials and they are considered to be promising lead-free ferroelectric materials because of their relatively high piezoelectric properties in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. The purpose of this work was to clarify the local structures of Li-substituted Bi
perovskite ferroelectric materials and they are considered to be promising lead-free ferroelectric materials because of their relatively high piezoelectric properties in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. The purpose of this work was to clarify the local structures of Li-substituted Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO and NaNbO
and NaNbO to elucidate the mechanism of the stabilization of the ordered ferroelectric phase.
to elucidate the mechanism of the stabilization of the ordered ferroelectric phase.
Ishikawa, Norito
no journal, ,
Ion-tracks are continuous columnar defects created along trajectories of high-energy ions. The electronic stopping power is one of the main parameters that dominate the size of the ion-track. Its size is an increasing function of Se if the ion-velocity is fixed. Moreover, in most of the oxides the ion-track size also depends on whether the ion-velocity is in low velocity regime or in high velocity regime. The ion-track size for low velocity ions is larger than that for high velocity ions, if Se is fixed. Such velocity-dependent effect is called the velocity effect. In the present talk, our experimental results on the irradiation effects in relation to the velocity effect in various ion-irradiated oxides will be presented. Recently, we found the velocity effect is absent in Se-dependence of ion-track size in ion-irradiated UO .
.
 using resonant X-ray emission at Ba L
using resonant X-ray emission at Ba L and Ti K edges
and Ti K edgesYoshii, Kenji; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Jarrige, I.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Nishihata, Yasuo; Suzuki, Chikashi; Ito, Yoshiaki*; Yoshikado, Shinzo*; Fukushima, Sei*
no journal, ,
We have studied the electronic properties of the ferroelectric barium titanate BaTiO using resonant X-ray emission spectroscopy (RXES) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy in the partial fluorescence mode (PFY-XAS) at the Ba L
using resonant X-ray emission spectroscopy (RXES) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy in the partial fluorescence mode (PFY-XAS) at the Ba L and Ti K absorption edges. Contrary to a previous study, we found no fine structure in the pre-edge area of the PFY-XAS spectrum at the Ba L3 edge, and no temperature-induced spectral change was observed across the Curie temperature (130
and Ti K absorption edges. Contrary to a previous study, we found no fine structure in the pre-edge area of the PFY-XAS spectrum at the Ba L3 edge, and no temperature-induced spectral change was observed across the Curie temperature (130 C). This result is not supportive of the possible presence of the displacement around Ba
C). This result is not supportive of the possible presence of the displacement around Ba at the Curie temperature. RXES spectra were measured at the Ti K edge. The photon energy of the emission peak is found to be nearly constant throughout the absorption edge for all three compounds. We deduce the Ti 3d states to have a delocalized character, in contrast with the Ba 5d states, a property which is consistent with the proposed scenario of the formation of electric dipoles in BaTiO
at the Curie temperature. RXES spectra were measured at the Ti K edge. The photon energy of the emission peak is found to be nearly constant throughout the absorption edge for all three compounds. We deduce the Ti 3d states to have a delocalized character, in contrast with the Ba 5d states, a property which is consistent with the proposed scenario of the formation of electric dipoles in BaTiO .
.
Owada, Kenji; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Mizuki, Junichiro*
no journal, ,
It is generally known that the temperature dependence of the dielectric constants of relaxor ferroelectrics near morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) shows a cooling-rate dependence. This is due to a domain fluctuation across a tetragonal-to-rhombohedral phase transition. In this paper, we focus on the tetragonal-to-rhombohedral phase transition (T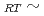 300 K) in relaxor ferroelectrics PZN-9%PT, which is very close to MPB. We have simultaneously measured the frequency-dependent dielectric constants and the coherent X-ray scattering directly reflecting a domain configuration. The results directly show an effect of the domain fluctuation on a low-frequency dielectric permittivity. These results should strongly relates to the cooling-rate dependence on the temperature dependence of the dielectric constants.
300 K) in relaxor ferroelectrics PZN-9%PT, which is very close to MPB. We have simultaneously measured the frequency-dependent dielectric constants and the coherent X-ray scattering directly reflecting a domain configuration. The results directly show an effect of the domain fluctuation on a low-frequency dielectric permittivity. These results should strongly relates to the cooling-rate dependence on the temperature dependence of the dielectric constants.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Maekawa, Yasunari; Voss, K.-O.*; Severin, D.*; Seidl, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The possibility of varying the beam parameters and applying the effect of a pre-etching treatment for poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) ion-track membranes was investigated with the goal of achieving enhanced track etching for effective control of the pore size and shape. Commercially available 25  m-thick PVDF films were irradiated at room temperature with swift heavy ions. Irradiation with a higher-LET beam gave faster track etching and larger pores, suggesting that the LET could be the most crucial factor determining the pore size. In-situ infra-red absorption and residual gas analyses shed light on the detailed chemistry of not only the ion-induced degradation, but also post-irradiation reactions. The pre-etching treatment effect involved oxidation of the unsaturated bonds within the latent track, which accelerated the chemical dissolution for efficient pore evolution. In other words, exposure to a gaseous oxidant, i.e., ozone, shortened the breakthrough time.
m-thick PVDF films were irradiated at room temperature with swift heavy ions. Irradiation with a higher-LET beam gave faster track etching and larger pores, suggesting that the LET could be the most crucial factor determining the pore size. In-situ infra-red absorption and residual gas analyses shed light on the detailed chemistry of not only the ion-induced degradation, but also post-irradiation reactions. The pre-etching treatment effect involved oxidation of the unsaturated bonds within the latent track, which accelerated the chemical dissolution for efficient pore evolution. In other words, exposure to a gaseous oxidant, i.e., ozone, shortened the breakthrough time.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kanazawa, Shinichi*; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Poly(L-lactic acid), [PLLA] one of bioplastics, is the most attractive materials because it is the most promising candidate for replacement of petrochemical plastics from the viewpoint of the global warming protection. The heat resistance property of PLLA has been improved by radiation-induced crosslinking with triallyl isocyanurate (TAIC). The applications of crosslinked PLLA, however, are limited, because the lack of flexibility is nearly un-improved. The plastics are currently soften by adding plasticizers. However, the plasticizer exudes from PLLA because of recrystallization even at room temperature, and PLLA becomes hard consequently with cloudiness. To solve the problem and expand further the applications of PLLA, effect of additive plasticizers on radiation-crosslinking of PLLA with TAIC and retention capacity in crosslinked PLLA were investigated. The crosslinking structures were formed in electron beam-irradiated PLLA with 3 phr (per hundred resin) TAIC and various content of plasticizer (acetylated monoglycerides or adipate ester mixture). The gel content of PLLA increased with the mixing ratio of the plasticizer and absorbed dose. At the dose of 20 kGy and more, the network was formed about 90% in the crosslinked PLLA. The plasticizer didn't exude from the crosslinked PLLA even if heated for a week at 80  C because of non-recrystallization, and so the crosslinked PLLA kept transparency. Improvement of elasticity was succeeded by adding high concentrated plasticizer (
C because of non-recrystallization, and so the crosslinked PLLA kept transparency. Improvement of elasticity was succeeded by adding high concentrated plasticizer ( 35%) in PLLA. Therefore, the applications of bioplastic will be expanded by the combination method of the radiation-induced crosslinking and adding high content of the plasticizer.
35%) in PLLA. Therefore, the applications of bioplastic will be expanded by the combination method of the radiation-induced crosslinking and adding high content of the plasticizer.
Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
Taking advantage of various quantum beams, we have developed polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs) for fuel cell hybrid vehicles. By radiation-induced graft polymerization, fluorinated-polymer-based PEM, which showed high power generation and mechanical properties under low and high humidity conditions, were successfully prepared. The anion-type PEMs having high alkaline-durability, which can be applied for platinum free alkaline fuel cells, can be prepared by the same methodology. Furthermore, several X-ray scattering measurements revealed the hierarchical structures which originated the superior mechanical and conducting properties of the PEMs.
Kikuchi, Tatsuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yoshimura, Kimio; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Shishitani, Hideyuki*; Yamaguchi, Susumu*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Ogiwara, Kiyoshi*; Yamazaki, Yasunori*
no journal, ,
We prepared platinum (Pt) nanoparticles by proton (H ) irradiation in liquid. The irradiation was performed by a tapered glass capillary with a thin lid at the tip. A beam of 3 MeV H
) irradiation in liquid. The irradiation was performed by a tapered glass capillary with a thin lid at the tip. A beam of 3 MeV H ion beam was focused and guided by small angle scatterings with an inner wall of the glass capillary, which was inserted in an aqueous solution of 1 mmol/L hexachloroplatinic(IV) acid and 10 vol% ethanol. The irradiation caused a formation of the Pt nanoparticles floating around the capillary tip. A size of the nanoparticles was estimated at 5-10 nm by transmission electron microscopy. The glassy-carbon substrate was then set in the solution perpendicular to the beam at the distance of 100
ion beam was focused and guided by small angle scatterings with an inner wall of the glass capillary, which was inserted in an aqueous solution of 1 mmol/L hexachloroplatinic(IV) acid and 10 vol% ethanol. The irradiation caused a formation of the Pt nanoparticles floating around the capillary tip. A size of the nanoparticles was estimated at 5-10 nm by transmission electron microscopy. The glassy-carbon substrate was then set in the solution perpendicular to the beam at the distance of 100  m and irradiated with the same beam. This gave the Pt nanoparticles supported uniformly on the substrate surface.
m and irradiated with the same beam. This gave the Pt nanoparticles supported uniformly on the substrate surface.
 -Ray Irradiation and Adsorption Properties of Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamate
-Ray Irradiation and Adsorption Properties of Zinc bis dimethyldithiocarbamateKo, B.-S.*; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sinananwanich, W.*; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
Diallyl phthalate-contained 1-Allyl-2-thiourea (FDA/ATU) was chemically combined on the poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) (PSD) particle surface by  ray irradiation method. The adsorption of zinc ions was found to increase with increasing the amount of ATU on the PSD particles. The adsorption of zinc ions was strongly dependent of the pH, and the maximum effect was demonstrated in the region of pH 5-7. At pH 7, the amount of zinc adsorption increased 2.64 times compared with the untreated PSD particles. The adsorbed zinc ions adsorbed on the modified PSD particles suppressed the decomposition of Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) (Ziram), and thus increased its adsorption capacity. In addition, the FDA/ATU-modified PSD particles could be used repeatedly with a high level of the Ziram adsorption and recovery ability. Therefore, a simple and quick solid phase adsorption process of the Ziram analysis could be established using the FDA/ATU-modified PSD particles.
ray irradiation method. The adsorption of zinc ions was found to increase with increasing the amount of ATU on the PSD particles. The adsorption of zinc ions was strongly dependent of the pH, and the maximum effect was demonstrated in the region of pH 5-7. At pH 7, the amount of zinc adsorption increased 2.64 times compared with the untreated PSD particles. The adsorbed zinc ions adsorbed on the modified PSD particles suppressed the decomposition of Zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) (Ziram), and thus increased its adsorption capacity. In addition, the FDA/ATU-modified PSD particles could be used repeatedly with a high level of the Ziram adsorption and recovery ability. Therefore, a simple and quick solid phase adsorption process of the Ziram analysis could be established using the FDA/ATU-modified PSD particles.